Dendritic cell-based therapies for cancer treatment
Viable dendritic cells with up to twice as capacity to boost antigen-specific anti-tumour and anti-viral activity
BACKGROUND
Dendritic cells (DCs) are key players in setting the immune system because they have an important role in antigen screening, uptake and presentation to T cells, ultimately triggering the adaptive response. Due to this prominent role, DCs are used as immunotherapies for different clinical indications, like cancer, autoimmune diseases or pathogen infection. However, DCs’ efficacy has shown to be limited to only a subset of patients, and it is urgent to boost their effectiveness and broaden their applicability. Sialic acids are post-translational modifications of several proteins and its content change along with cell differentiation and activation, having important implications in cell ‘s functions. Sialic acids have a crucial role in immune modulation due to its recognition by lectin receptors, most of them with inhibitory endeavours. Moreover, changes in sialic acid content are associated with diseases as cancer, where oversialylation assumes to be a hallmark of cancer.
TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW
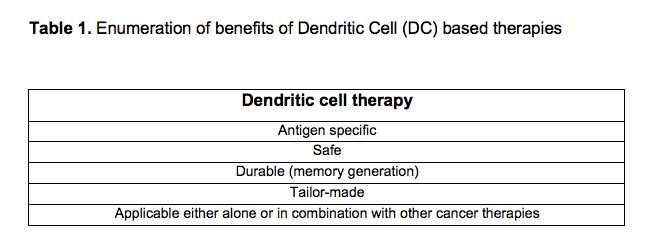
This patent-protected technology uses the manipulation of DC surface sialic acids to impact critical DC functions and is an innovative method to tackling the lack of efficacy of current immunotherapies, to improve and diversify DC-based therapies. Dendritic cells are antigen-specific, safe, long-lasting tailor-made immunotherapies. These innovative immunotherapies are very versatile and can be applied alone or in combination with other therapies to treat any cancer type at any stage (early to metastatic) (Table 1).
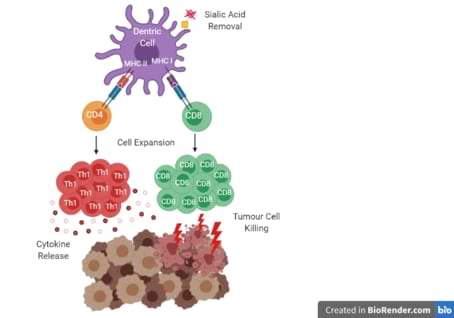
The patent-protected technology (Figure 1):
- Drives stronger proper DC maturation;
- Drives higher lymphocyte T cell Polarization toward cancer elimination;
- Ameliorates the synapses of DCs with T cells;
- Improves cross-presentation; a crucial mechanism for the effective presentation of tumor-associated antigens to CD8+ T-cell responses.
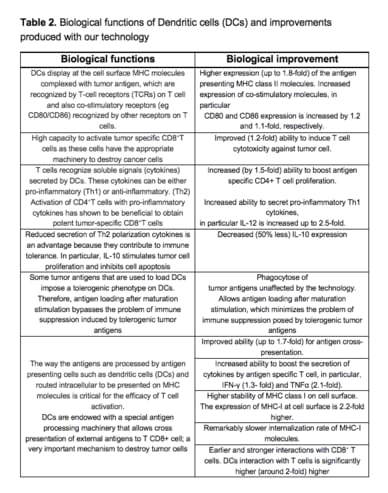
More details for biological improvements are described in Table 2.
FURTHER DETAILS
- Silva M, Silva Z, Marques G, Ferro T, Gonçalves M, Monteiro M, van Vliet S, Mohr E, Lino AC, Fernandes AR, Lima FA, van Kooyk Y, Matos T, Tadokoro CE and Videira PA. Sialic acid removal from dendritic cells improves antigen cross-presentation and boosts anti-tumor immune responses. Oncotarget. 2016. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9419. (a patent application was filed prior to the publication date);
- Silva Z, Ferro T, Almeida D, Soares H, Ferreira J A, van Vliet S J, Springer S, Videira P A. MHC class I stability is modulated by cell surface sialylation in human dendritic cells. Submitted to Pharmaceutics.
STAGE OF DEVELOPMENT
TLR 4 – Technology developed in laboratory.
BENEFITS
- Simple one step enzymatic reaction which reduces production costs compared to other strategies, i.e. cytokine cocktail;
- Can be applied before loading of antigens, therefore preventing/bypassing antigen-driven immune suppression;
- Applicable to any type of antigen or any type vehicle;
- Applicable to cells from various sources;
- Applicable to different DC fabrication protocols;
- Improves antigen cross-presentation;
- Applicable to different DC based therapies;
- Allows combining DCs with other immunotherapies;
- Can be used to control DC immunogenicity and balance between autoimmunity and cancer therapy.
APPLICATIONS
Vaccine market; immunotherapies;
- Peripheral Blood plasmacytoid cells;
- Peripheral Blood myeloid precursor;
- Langerhans cells;
- Cord blood;
- Bone marrow.
OPPORTUNITY
Seeking investors support or industrial partnership to carry out further clinically relevant development.
Available for exclusive and non-exclusive licensing.
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY
- WO2017002045
-
BR112018000027
NOVA Inventors
Paula Alexandra Videira
Mariana Araújo Alves Martins da Silva
Graça S. Marques
Zélia Maria Cordeiro da Silva


