
Phenylpropanoid saccharide esters, methods and uses thereof
Phenylpropanoid saccharide esters with different degrees and place of substitution, and their use as antimicrobial and cytotoxic agents
BACKGROUND
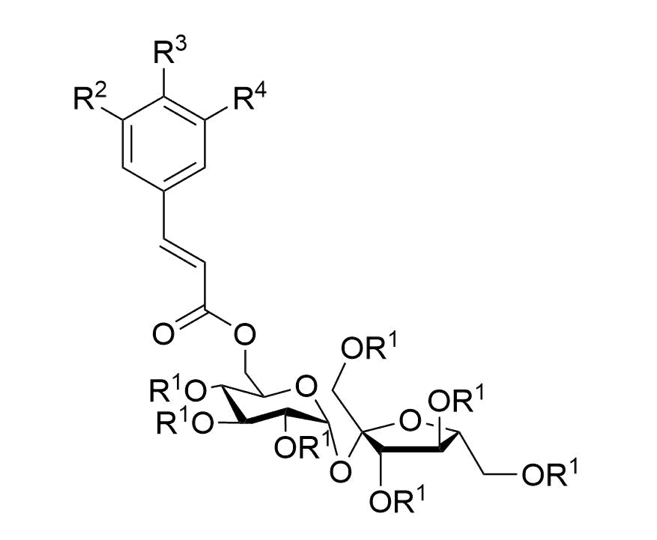
It is widely recognized that lead compounds from natural sources are valuable resource for developing novel drugs to face the rising health challenges of the modern world. During the last decades, more than 150 phenylpropanoid sucrose esters have been isolated and identified from plants used in folk medicine since antiquity, which have been reported to possess antioxidative, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties, among other pharmacological activities.
Their synthesis has not been achieved so far, which, combined with the milligram quantities isolated from plants in pure form, has prevented their use in pharmacology. In order to avoid lengthy protection/deprotection methodologies, normally followed in carbohydrate chemistry, it is proposed a novel methodology to synthesize these active compounds and their analogues, based on a chemoselective one-step procedure.
TECHNOLOGY OVERVIEW
Methods for the synthesis of a library of phenylpropanoid saccharide esters were developed, and their antibacterial, antifungal and cytotoxic activities were demonstrated for applications in the industry.
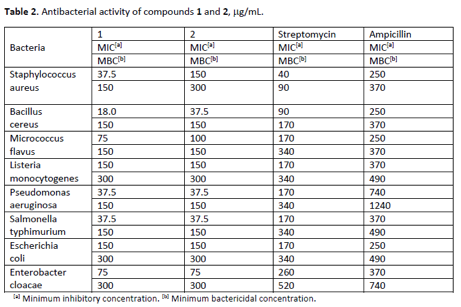
The lead compounds exhibited strong inhibition against all bacteria tested, namely Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus cereus, Micrococcus flavus, Listeria monocytogenes, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Salmonella typhimurium, Escherichia coli and Enterobacter cloacae and strong antifungal activity towards Aspergillus versicolor, Aspergillus ochraceus, Trichoderma viride and Penicillium ochrochloron. They showed moderate antioxidant and antitumor potential against human breast, colon and cervical cell lines without hepatotoxicity. The synthesized product can be obtained in larger quantities and at cheaper price comparing to the extracted one and thus could find application in various pharmacological compositions.
STAGE OF DEVELOPMENT
TRL 4 – Technology Validated in Laboratory.
BENEFITS
Because of the small quantities isolated from plants, the pharmacological properties of the naturally occurring phenylpropanoid saccharide esters have not been extensively studied and they have not find applications in pure form so far. With the presented chemical synthesis, large amounts of these compounds will be available and they could be applied in the pharmacological, cosmetics and food industries.
The invention presents newly discovered biological activities of these compounds as well.
APPLICATIONS
This technology has the potential to provide the basis for new antimicrobial therapeutics or novel ingredients for cosmetic or even food and products.
OPPORTUNITY
These compounds can find applications as antibacterial, antifungal, antioxidant or cytotoxic agents in pharmacology and cosmetology. NOVA seeks industrial support/collaboration to carry out further, clinically relevant development, including:
- Scale-up of the synthesis;
- Further compound optimization from a medicinal chemistry perspective;
- Toxicity tests;
- Further in vitro tests;
- In vivo studies.
INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY
SEEKING
- Licensing.
- Development partner.
NOVA Inventors
Krasimira Petrova


